Un- like bacteria eukaryotes initiate chromosome replication in a temporally. The DNA replication in prokaryotes takes place in the following place.
Steps Involved In Dna Replication In Prokaryotes E Coli
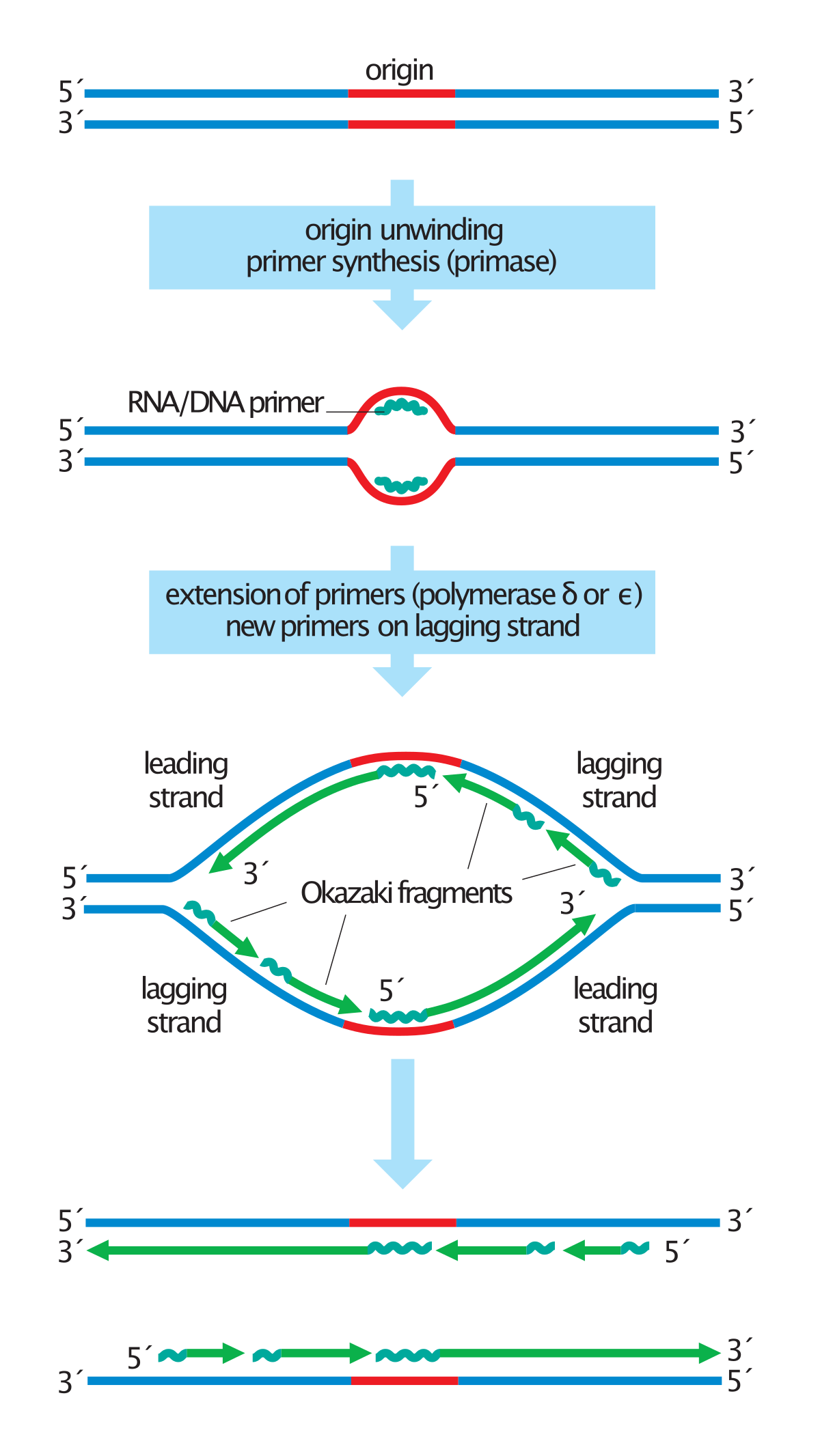
Okazaki Fragments Wikipedia
Pdf Dna Replication
And how these processes differ in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.

Dna replication in prokaryotes pdf. Both strands are synthesized simultaneously by. DNA Replication Prokaryotes. Eukaryotic DNA Replication Fidelity 219 tials for various combinations of dNTPs and template bases sequence- dependent differences in base stacking and a demand for equivalent base-pair geometry for review see Echols and Goodman 1991.
Once the tRNA donated its amino acid it exits the ribosome. While all forms of life replicate DNA in a similar manner higher order organisms tend to have more proteins and enzymes involved in the process with complex mechanisms poorly. The DNA is coated by the single-strand binding proteins around the replication fork to prevent rewinding of DNA.
TRNAs charged with amino acids enter the ribosomes where their amino acid is transferred on to the growing polypeptide chain. Fangman and Brewer 1992. DNA replication is a core biological process that occurs in prokaryotic cells at high speeds 1 nucleotide residue added per millisecond and with high fidelity fewer than one misincorporation.
Escherichia coli has 46 million base pairs in a single circular chromosome and all of it gets replicated in approximately 42 minutes starting from a single origin of replication and proceeding around the chromosome in both directions. Unlike in eukaryotes pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotides are synthesized from ribonucleotide diphosphates rather than triphosphates. DNA is synthesized in the replication fork in 5 to 3 direction Leading strand synthesis is continuous whereas lagging strand is synthesized in fragments.
Semi-conservative Replication is catalyzed by DNA Polymerase. The initial loading of the replication machinery known as orisome a nuclear-protein complex and the initial unwinding takes place at origin. Because each strand can be.
Length of Okazaki fragments in prokaryotes are 1000-2000 nt in eukaryotes 100-200 nt. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells contain multiple DNA polymerase activities 3. Evolved extremely intricate DNA replication machinery which can respond to varied external and internal signals 13.
1 Recognition of origin. DNA replication in prokaryotes. Principles of Biology contents 45 DNA Replication Figure 1.
Describe how errors occur during replication how they are repaired and the consequences of failure to repair such errors. DNA replication begins from origin. Helicase opens up the DNA double helix resulting in the formation of the replication fork.
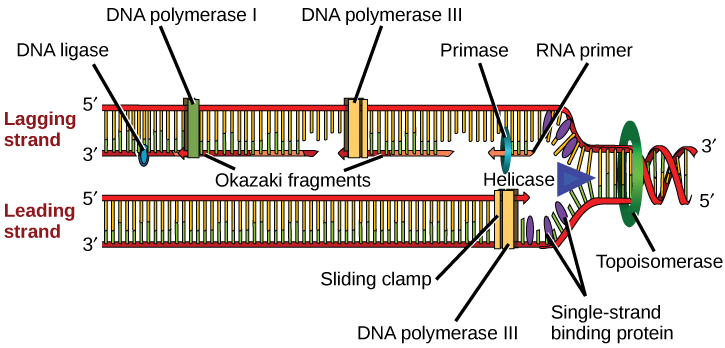
The following points highlight the three main phases of DNA replication in prokaryotes. ÐPol III Ð produces new stands of complementary DNA ÐPol I Ð fills in gaps between newly synthesized Okazaki segments additional enzymesproteins Ði DNA helicase Ð unwinds double helix Ðii Single-stranded binding proteins Ð keep helix open. Replication initiation involves the following events.
Single-strand binding proteins bind to the single-stranded DNA near the replication fork to keep the fork open. View DNA replication in prok. As the DNA opens up Y-shaped structures called replication forks are formed.
Two copies of an enzyme called helicase are among the proteins recruited to the origin. Coli chromosomal DNA replication initiates at origin of. The mechanism of DNA replication prokaryotic DNA polymerase Ðthe enzyme that extends the primer.
Each helicase unwinds and separates the DNA helix into single-stranded DNA. In the well-studied bacteria Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis this occurs in the terminus region which is situated diametrically opposite the origin. The first proteins to bind the DNA are said to recruit the other proteins.
Mistakes during DNA synthesis are edited. Only few of them actually undertake replication. DNA REPLICATION IN PROKARYOTES Submitted ByMoumita Paul Roll No.
Replication in prokaryotes starts from a sequence found on the chromosome called the origin of replicationthe point at which the DNA opens up. Initiation elongation and termination and the commonality runs through all types of living cellular-based organisms. 8 Once the ribosome is assembled the translation of the mRNA is initiated from a start codon AUG on the mRNA.
Lesson Summary Copying the Code Each strand of the double helix has all the information needed to reconstruct the other half by the mechanism of base pairing. DNA replication involves three distinct phases. 123 DNA Replication Lesson Objectives Summarize the events of DNA replication.
The prokaryotic cell usually has one origin as the genome is small and circular. Possible mechanisms for DNA replication. Helicase opens the DNA and replication forks are formed.
Termination of DNA replication occurs when the two forks meet and fuse creating two separate double-stranded DNA molecules. The genetic material must be faithfully replicated to assure heredity. The replication takes place in a semi-conservative manner semi-conservative replication.
Compare DNA replication in prokaryotes with that of eukaryotes. These enzymes are some times called as replicases. DNA Replication Process in Prokaryotes.
For the three viral DNA polymerases mentioned above the. The two strands of DNA unwind at the origin of replication. Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA Replication 437 of individual eukaryotic chromosomes replicate at distinct times during S phase demonstrating that multiple origins of DNA replication must exist Hand 1978.
Explain how telomeres are replicated in eukaryotic cells. B Bidirectional DNA replication occurs through the cleavage of the displaced solid blue circle strand of DNA followed by formation of two replication forks. DNA replication occurs by three steps.
BASIC COMPONENTS OF DNA REPLICATION MACHINERY DNA replication is initiated at specific loci on the template DNAs. Summarypdf from BISC 403 at University of Delaware. The replication of DNA initiates at a particular sequence of nucleotides in the genome known as origin.
This has been most clearly shown in prokaryotes in which replication origins have been defined unambiguously as. DNA replication has been extremely well-studied in prokaryotes primarily because of the small size of the genome and large number of variants available.

Dna Replication In Prokaryotes

Historical Perspective Of Eukaryotic Dna Replication Springerlink
6 6 Dna Replication In Prokaryotes Chemistry Libretexts

Dynamics Of Dna Replication In A Eukaryotic Cell Pnas

12 3 Dna Replication Ppt Download

Pdf Comparison Of Dna Replication In Cells From Prokarya And Eukarya Semantic Scholar
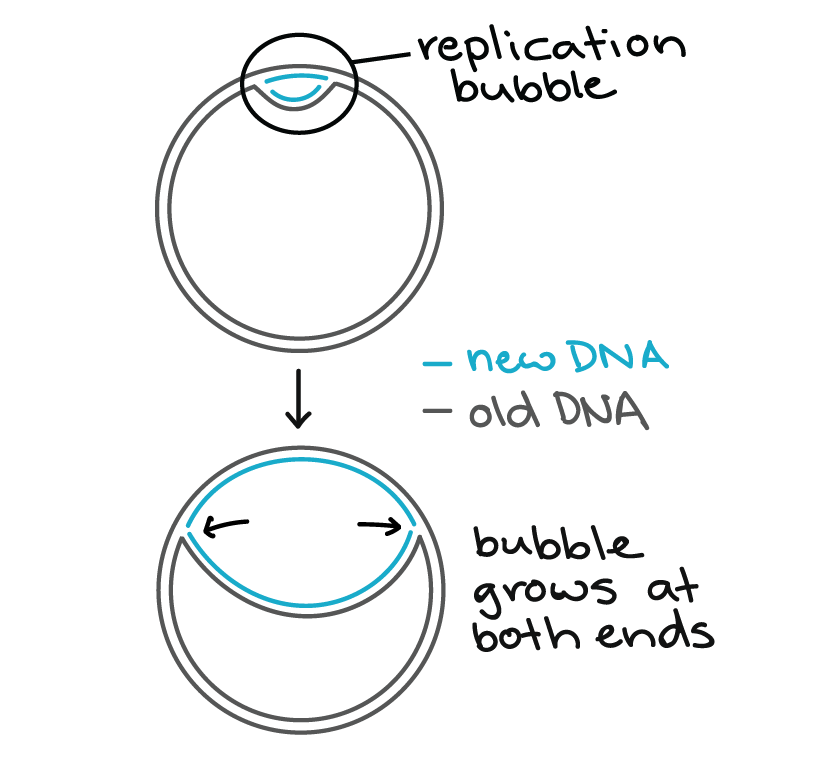
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy

Dna Replication Microbiology

